Ecodesign - ecological design
|
The Ecodesign is the methodology of the industrial products design, taking into account the environment during the process of development of the product, like an additional factor to those that traditionally are used for taking decisions: aesthetic design, cost, quality etc. Goals of the EcodesignThe goal of the ecodesing is double. On one hand consist on reducing the environmental impact of the product during their cycle of life. On the other hand, getting a benefit in return for the involved stakeholders and the final user of the product. Why to apply the Ecodesing?The factors for the application of the ecodesing in the definition phase and design of the product can be different: External reasons
Internal reasons
Methodologies of EcodesingThe projects of Ecodesing require an organizational vision where all the actors of the project collaborate and carry out their work simultaneously. This focus needs of some specifics tools and a special phase of planning designed for such aim. Next, the phases that compose two of the ecodesing methodologies more used are presented: PILOT methodology (original source)Ecodesign The phases of the PILOT metodology.
PROMISE Methodology
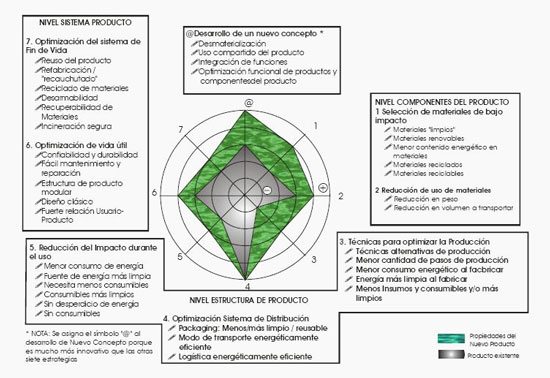
Methodology created in the 1994 by the Technological University of Delft that was taken as base for the manual of Ecodesing of the UNEP in 1997 (ECODESIGN: to promising approach to sustainable production and consumption). Ecodesign strategiesThe LIDS wheelBased on the LiDS Wheel, the different strategies are classified in the following groups:
Strategies of PILOTSimilar to the LiDS Wheel, PILOT proposes specific strategies for each phase of the life cycle of the product. For that, first of all it is necessary to analyze in which phases the most important negative impacts take place. Once carried out this analysis, the product is classified according to the following skills:
For example, a washer is a “type D” product. It produces its biggest negative impact during the phase of USE of the product. PILOT will offer specific strategies to reduce the consumption centred mainly in its use phase. Levels of EcodesingAlthough the ecodesing is able to innovate the systems or the products of a company radically, it can also propose simpler solutions, with short term results. Depending on the target establish by the company, four levels of application of the ecodesing can be distinguished, and therefore four types of different results:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Noticias
- Orange, Ricoh y Dídac Lee se llevan los Premios Excelencia 2015
- El empleo, la energía y el clima ejes del congreso de entidades locales CONAMA Local 2015
- El Gobierno Vasco subvenciona con 94 mil euros acciones que fomenten la movilidad activa en la población escolar
- La gestión de Residuos de Equipos Eléctrico Electrónicos (RAEE) en España sigue mejorando gracias a la Fundación Ecolec
Environmental services
Our company offers environmental engineering solutions, ecodesign and all type of projects for the sustainable development of the companies.

Sustainable development
"To satisfy the necessities of the present without committing the capacity of the future generations to satisfy their own necessities".

With this definition we offer our consultantship services in sustainable development.
Contact
Contact address:
c/ Beheko Kale nº13 Bajo
CP 01.170 Legutio (Álava)
Tel: 945 455905
Fax: 945 455930
ecolan@ecolaningenieria.com